Understanding the taxonomy of AI!
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing the way we interact with technology, impacting various industries from healthcare to finance.
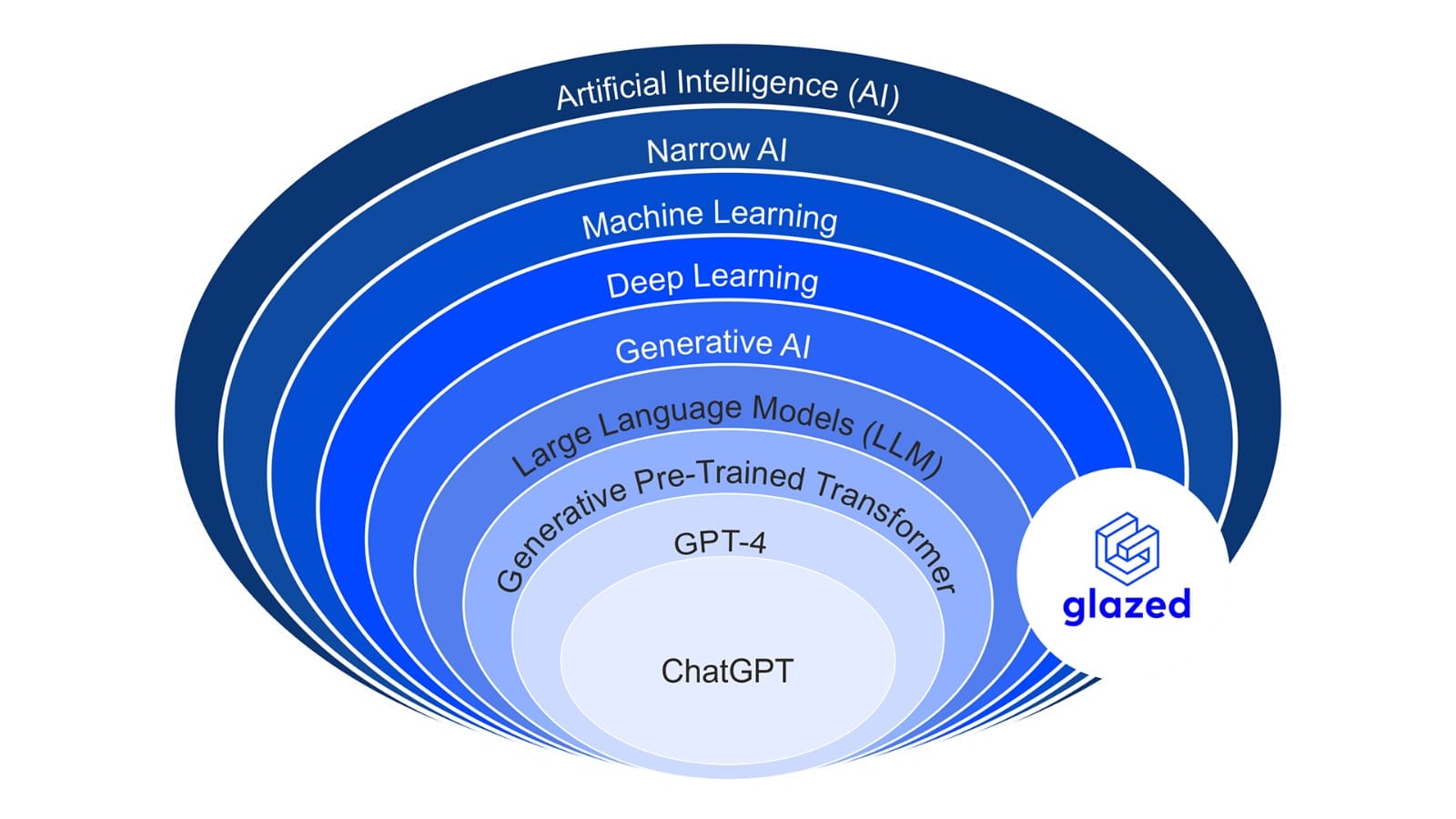
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing the way we interact with technology, impacting various industries from healthcare to finance. However, AI is not a monolithic entity; it comprises a vast array of technologies, each with distinct characteristics and applications. Understanding the taxonomy of AI—how these technologies are categorized and related—provides a clearer picture of the AI landscape and its capabilities.
This taxonomy helps us differentiate between various types of AI systems, from narrow AI designed for specific tasks to the ambitious goals of general AI. It also encompasses the methodologies that drive AI, such as machine learning and deep learning, and delves into specific implementations like generative AI and large language models. By exploring these categories, we gain insight into how AI technologies are developed, how they function, and how they can be applied to solve real-world problems.
This structured approach not only aids in understanding the current state of AI but also prepares us for the rapid advancements and emerging trends in the field. Whether you are a student, a professional, or simply curious about AI, comprehending its taxonomy is essential for appreciating the breadth and depth of artificial intelligence and its transformative potential.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
At the broadest level, Artificial Intelligence encompasses all techniques and methods that enable machines to mimic human intelligence. AI aims to create systems capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as reasoning, learning, and problem-solving.
Narrow AI
Narrow AI, also known as Weak AI, refers to AI systems designed to perform a specific task or a narrow range of tasks. These systems operate under a limited set of constraints and do not possess general intelligence. Examples include voice assistants like Siri and Alexa, as well as recommendation algorithms used by Netflix and Amazon.
Machine Learning
Machine Learning (ML) is a subset of AI focused on developing algorithms that allow computers to learn from and make predictions based on data. ML algorithms can identify patterns and make decisions with minimal human intervention. The primary types of machine learning include supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning.
Deep Learning
Deep Learning is a specialized subset of machine learning that uses neural networks with many layers (hence "deep") to model complex patterns in large datasets. It is particularly effective in tasks such as image and speech recognition, natural language processing, and autonomous driving. Deep learning algorithms are inspired by the structure and function of the human brain.
Generative AI
Generative AI refers to algorithms that can generate new content based on the data they have been trained on. This includes creating text, images, music, and even video. Generative AI models learn the underlying distribution of the training data and can produce new instances that resemble the training set.
Large Language Models (LLM)
Large Language Models are a type of generative AI specifically designed to understand and generate human language. These models, such as GPT-3 and GPT-4, are trained on vast amounts of text data and can perform a wide range of language-related tasks, from translation and summarization to conversational agents.
Generative Pre-Trained Transformer
The Generative Pre-Trained Transformer (GPT) is a specific architecture for building large language models. It uses a transformer architecture, which relies on self-attention mechanisms to process input data efficiently. GPT models are pre-trained on extensive text corpora and can be fine-tuned for specific tasks.
GPT-4
GPT-4 is the latest iteration of the Generative Pre-Trained Transformer series, known for its advanced language understanding and generation capabilities. It represents a significant leap forward in AI's ability to engage in natural language conversations, understand context, and produce coherent and contextually relevant text.
ChatGPT
ChatGPT is an application of the GPT-4 model, specifically designed for conversational interactions. It can understand and generate human-like responses, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, from customer support to virtual assistants. ChatGPT leverages the extensive training of GPT-4 to provide engaging and context-aware conversations.
I hope this article gave you a good overview of some key AI concepts and how they are connected.
As you continue to interact with AI, feel free to come back to these explanations and keep in mind the potential applications and limitations of these technologies.
Thanks for reading. If you enjoyed our content you can you can stay up to date by following us on Twitter, Facebook and LinkedIn 👋


